Tutorial for Mesh
The Mesh entity is a 3D object in WCS build up
from vertices and faces.
Create a cube mesh by directly accessing the base data structures:
import ezdxf
# 8 corner vertices
cube_vertices = [
(0, 0, 0),
(1, 0, 0),
(1, 1, 0),
(0, 1, 0),
(0, 0, 1),
(1, 0, 1),
(1, 1, 1),
(0, 1, 1),
]
# 6 cube faces
cube_faces = [
[0, 1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6, 7],
[0, 1, 5, 4],
[1, 2, 6, 5],
[3, 2, 6, 7],
[0, 3, 7, 4]
]
# MESH requires DXF R2000 or later
doc = ezdxf.new("R2000")
msp = doc.modelspace()
mesh = msp.add_mesh()
# do not subdivide cube, 0 is the default value
mesh.dxf.subdivision_levels = 0
with mesh.edit_data() as mesh_data:
mesh_data.vertices = cube_vertices
mesh_data.faces = cube_faces
doc.saveas("cube_mesh_1.dxf")
Create a cube mesh by assembling single faces using the
edit_data() context manager of the
Mesh class and the helper class
MeshData:
import ezdxf
# 8 corner vertices
p = [
(0, 0, 0),
(1, 0, 0),
(1, 1, 0),
(0, 1, 0),
(0, 0, 1),
(1, 0, 1),
(1, 1, 1),
(0, 1, 1),
]
# MESH requires DXF R2000 or later
doc = ezdxf.new("R2000")
msp = doc.modelspace()
mesh = msp.add_mesh()
with mesh.edit_data() as mesh_data:
mesh_data.add_face([p[0], p[1], p[2], p[3]])
mesh_data.add_face([p[4], p[5], p[6], p[7]])
mesh_data.add_face([p[0], p[1], p[5], p[4]])
mesh_data.add_face([p[1], p[2], p[6], p[5]])
mesh_data.add_face([p[3], p[2], p[6], p[7]])
mesh_data.add_face([p[0], p[3], p[7], p[4]])
# optional call optimize(): minimizes the vertex count
mesh_data.optimize()
doc.saveas("cube_mesh_2.dxf")
Its recommended to use the MeshBuilder objects to
create 3D meshes and render them as MESH entities by the
render_mesh() method into a layout:
import ezdxf
from ezdxf import colors
from ezdxf.gfxattribs import GfxAttribs
from ezdxf.render import forms
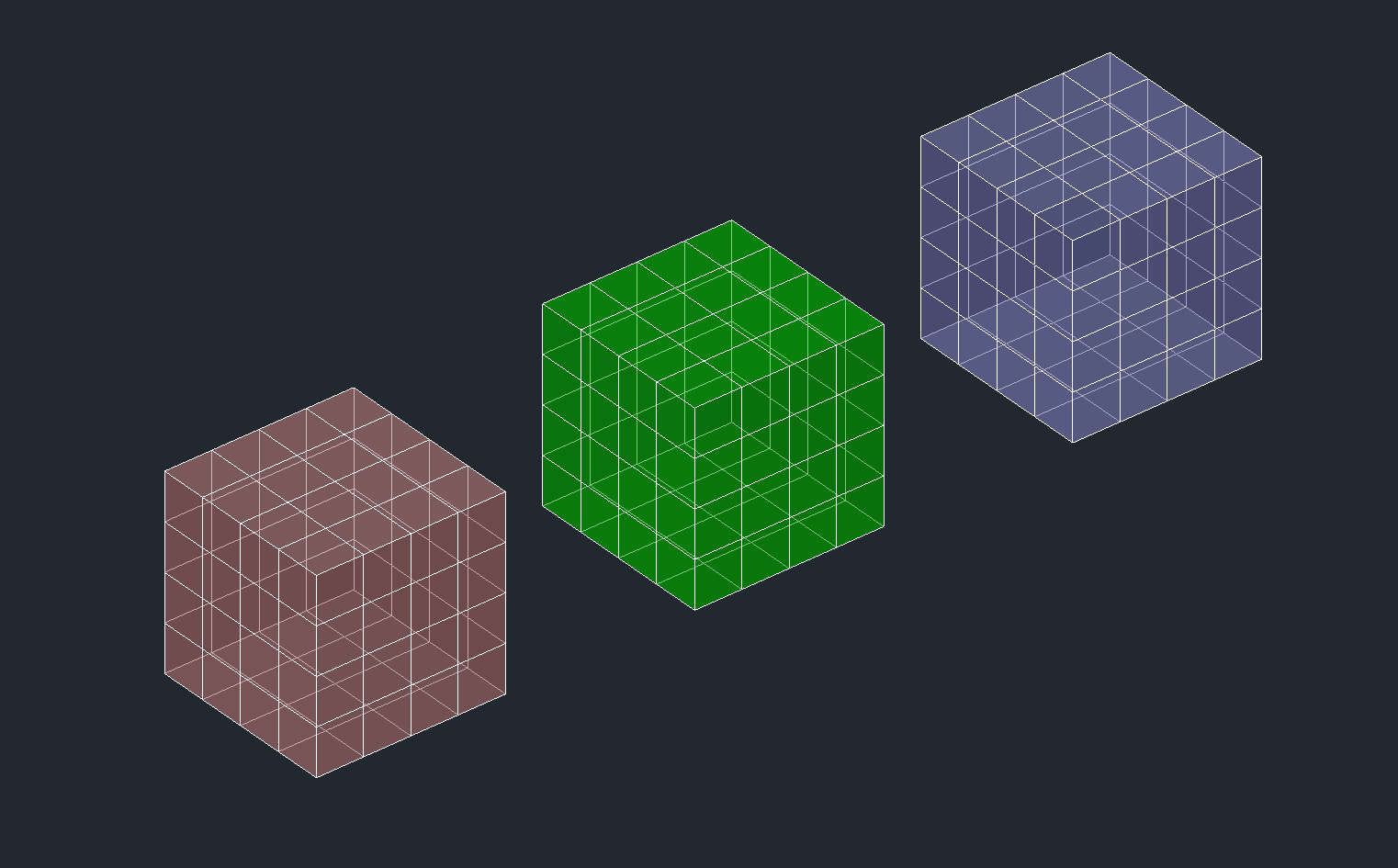
cube = forms.cube().scale_uniform(10).subdivide(2)
red = GfxAttribs(color=colors.RED)
green = GfxAttribs(color=colors.GREEN)
blue = GfxAttribs(color=colors.BLUE)
doc = ezdxf.new()
msp = doc.modelspace()
# render as MESH entity
cube.render_mesh(msp, dxfattribs=red)
cube.translate(20)
# render as POLYFACE a.k.a. POLYLINE entity
cube.render_polyface(msp, dxfattribs=green)
cube.translate(20)
# render as a bunch of 3DFACE entities
cube.render_3dfaces(msp, dxfattribs=blue)
doc.saveas("meshes.dxf")
There exist some tools to manage meshes:
ezdxf.render.MeshBuilder: TheMeshBuilderclasses are helper tools to manage meshes buildup by vertices and faces.ezdxf.render.MeshTransformer: Same functionality asMeshBuilderbut supports inplace transformation.ezdxf.render.MeshDiagnose: A diagnose tool which can be used to analyze and detect errors ofMeshBuilderobjects like topology errors for closed surfaces.ezdxf.render.FaceOrientationDetector: A helper class for face orientation and face normal vector detection
The ezdxf.render.forms module provides function to create basic
geometries like cube, cone, sphere and so on and functions to create meshes
from profiles by extrusion, rotation or sweeping.
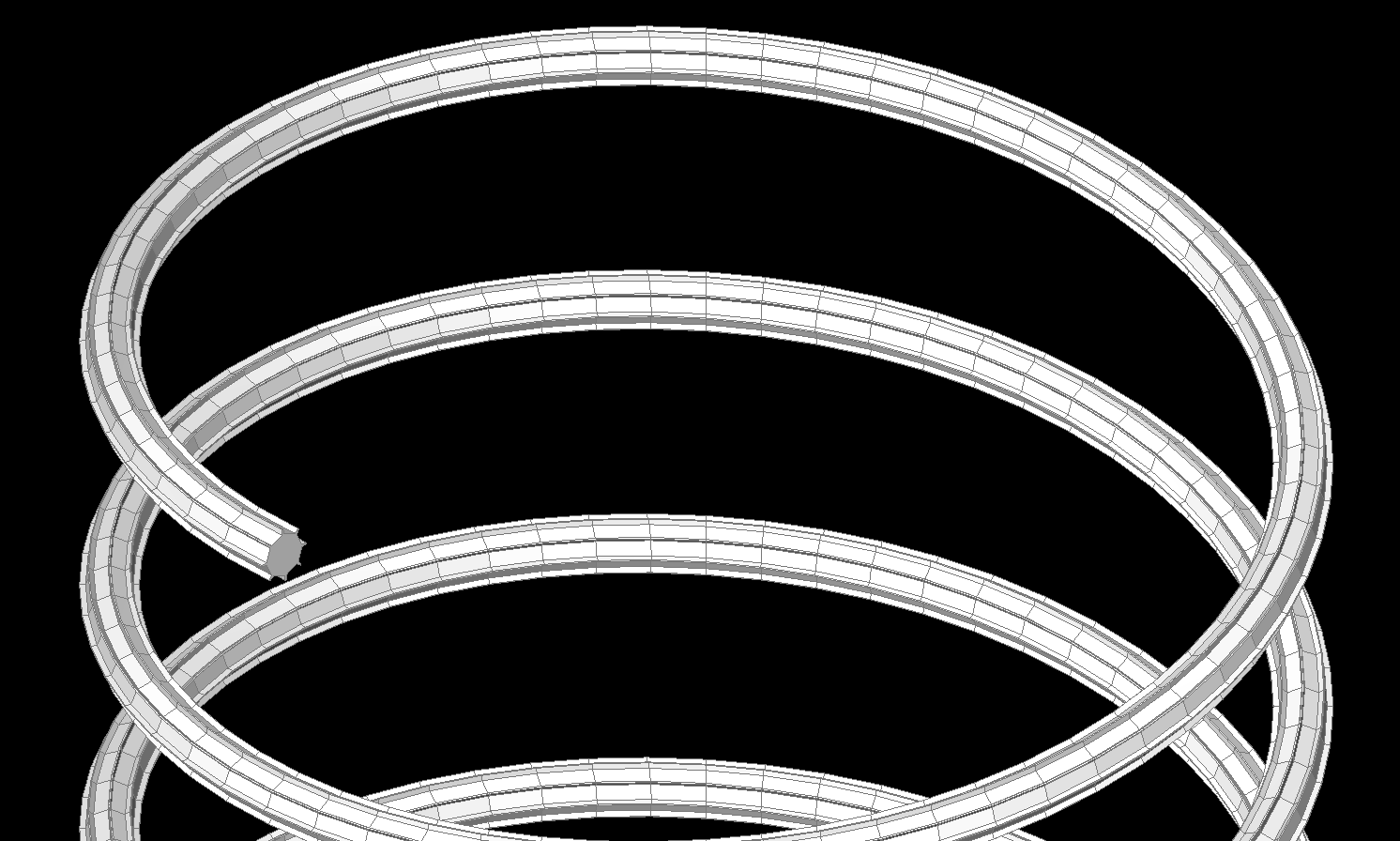
This example shows how to sweep a gear profile along a helix:
import ezdxf
from ezdxf.render import forms
doc = ezdxf.new()
doc.layers.add("MESH", color=ezdxf.colors.YELLOW)
msp = doc.modelspace()
# sweeping a gear-profile
gear = forms.gear(
8, top_width=0.01, bottom_width=0.02, height=0.02, outside_radius=0.1
)
helix = path.helix(radius=2, pitch=1, turns=6)
# along a helix spine
sweeping_path = helix.flattening(0.1)
mesh = forms.sweep(gear, sweeping_path, close=True, caps=True)
# and render as MESH entity
mesh.render_mesh(msp, dxfattribs={"layer": "MESH"})
doc.saveas("gear_along_helix.dxf")
